BNOSAC will be giving from June 08 up to June 12 a 5-day crash course on the use of R using Oracle R Enterprise. The course is given together with our Oracle Partner in Leuven, Belgium. If you are interested in attending, contact us for further details.
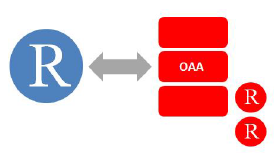
For R users who aren't aware of this yet. Oracle has embedded R into it's database which allows R users to transparently run R code inside the database - yes really transparently. The Oracle R Enterprise is part of the Oracle Advanced Analytics stack which basically consists of the following elements for R users:
- ROracle: supported native DBI driver to connect R with Oracle which is open source and available at CRAN (link).
- Oracle R Enterprise (ORE): This consists of an Oracle released version of R which is up to date with the current version of R and supported by Oracle and next to that a number of R packages which are available for download at the ORE website. These packages embed R into Oracle.
- Oracle Data Mining (ODM): a set of distributed data mining algorithms accessible from R
- Oracle Advanced Analytics for Hadoop (ORAAH) : a set of R packages which allow R users to connect with Hadoop and run data mining models and map reduce jobs on top of Hadoop. (link)
During the 5-day course, you will learn how to use R alongside the Oracle DB. The course covers some base R, advanced R usage and functionality from the Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) suite of packages. 
Module 1: Introduction to base R
What is R, packages available (CRAN, R-Forge, ...), R documentation search, finding help, RStudio editor, syntax, Data types (numeric/character/factor/logicals/NA/Dates/Times), Data structures (vector/data.frame/matrix/lists and standard operations on these), Saving (RData) & importing data from flat files, csv, Excel, Oracle, MS SQL Server, SAS, SPSS, Creating functions, data manipulation (subsetting, adding variables, ifelse, control flow, recoding, rbind, cbind) and aggregating and reshaping, Plotting in R using base and lattice functionality (dot plots, barcharts, graphical parameters, legends, devices), Basic statistics in R (mean, variance, crosstabs, quantile, correlation, distributions, densities, histograms, boxplot, t-tests, wilcoxon test, non-parametric tests)
Module 2: Advanced R programming & data manipulation with base R
vectorisation, writing your own functions, control flow, aggregating and data.table - fast group by, joining and data.table programming tricks, reshaping from wide to long format, miscellaneous usefull functions, apply family of functions & split-apply-combine strategy, do.call, parallel execution of code, handling of errors and exceptions, debugging code, other goodies: basic regular expressions, data manipulations, rolling data handling, S3 classes, generics and basic S4 methodology
Module 3: ROracle and Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) - transparancy layer
• ROracle - getting and sending SQL queries from Oracle
• Installing Oracle R Enterprise (ORE)
• Basic database connectivity: ore.exec, ore.ls, ore.synch, ore.push, ore.pull, ore.create, ore.drop, ore.get
• ORE data types: ore.character, ore.factor, ore.logical, ore.number, ore.datetime, ore.numeric. Conversion between data types
• ORE data structures: ore.matrix, ore.frame, ore.vector
• ORE transparancy data operations on ore.frame/ore.vector (subset, ncol, nrow, head, ifelse, paste, is.na, sd, mean, tapply, by, c, %in%, ...) and indexing and overwriting in-database ore.vectors
• Save R objects in Oracle ore.save, ore.load, ore.datastore and ORE data store handling
• Basic statistics with ORE (ore.univariate, ore.summary, ore.crosstab, ore.corr, exponential smoothing, t.test, wilcoxon, IQR)
Module 4: Oracle R Enterprise - advanced data manipulation
• Running R functions parallel inside the database: ore.doEval, ore.groupApply, ore.indexApply, ore.rowApply, ore.tableApply
• Creating R scripts inside the database and accessing ORE stored procedures
• Embedding R scripts in production database applications
• Embedded (parallel) R execution within ORE using the R Interface as well as the SQL Interface
Module 5: Data mining models inside Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) and Oracle Data Mining (ODM)
In this session you will become acquainted with some of the most common data mining methods and learn how to use these algorithms in ORE. The following algorithms will be covered.
• principal component analysis and factor analysis
• kmeans clustering and orthogonal partitioning
• data reduction using Minimum Description Length attribute importance
• linear models and generalized linear models
• naive bayes, neural networks, decision tree and support vector machines
• market basket analysis / recommendation engines (apriori)
• bagging
If you are interested in attending, contact us for further details.
We will be showcasing our RMOA package at the next R User conference in Aalborg.
For the R users who are unfamiliar with streaming modelling and want to be ahead of the Gartner Hype cycle or want to evaluate existing streaming machine learning models, RMOA allows to build, run and evaluate streaming classification models which are built in MOA (Massive Online Learning).
For an introduction to RMOA and MOA and the type of machine learning models which are possible in MOA - see our previous blog post or scroll through our blog page.
In this example below, we showcase the RMOA package by using streaming JSON data which can come from whatever noSQL database that spits out json. For this example, package jsonlite provides a nice stream_in function (an example is shown here) which handles streaming json data. Plugging in streaming machine learning models with RMOA is a breeze.
Let's dive into the R code immediately where we show how to run, build and evaluate a streaming boosted classification model.
require(jsonlite)
require(data.table)
require(RMOA)
require(ROCR)
##
## Use a dataset from Jeroen Ooms available at jeroenooms.github.io/data/diamonds.json
##
myjsondataset <- url("http://jeroenooms.github.io/data/diamonds.json")
datatransfo <- function(x){
## Setting the target to predict
x$target <- factor(ifelse(x$cut == "Very Good", "Very Good", "Other"), levels = c("Very Good", "Other"))
## Making sure the levels are the same across all streaming chunks
x$color <- factor(x$color, levels = c("D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J"))
x
}
##
## Read 100 lines of an example dataset to see how it looks like
##
x <- readLines(myjsondataset, n = 100, encoding = "UTF-8")
x <- rbindlist(lapply(x, fromJSON))
x <- datatransfo(x)
str(x)
######################################
## Boosted streaming classification
## - set up the boosting options
######################################
ctrl <- MOAoptions(model = "OCBoost", randomSeed = 123456789, ensembleSize = 25,
smoothingParameter = 0.5)
mymodel <- OCBoost(control = ctrl)
mymodel
## Train an initial model on 100 rows of the data
myboostedclassifier <- trainMOA(model = mymodel,
formula = target ~ color + depth + x + y + z,
data = datastream_dataframe(x))
## Update the model iteratively with streaming data
stream_in(
con = myjsondataset,
handler = function(x){
x <- datatransfo(x)
## Update the trained model with the new chunks
myboostedclassifier <- trainMOA(model = myboostedclassifier$model,
formula = target ~ color + depth + x + y + z,
data = datastream_dataframe(x),
reset = FALSE) ## do not reset what the model has learned already
},
pagesize = 500)
## Do some prediction to test the model
predict(myboostedclassifier, x)
table(sprintf("Reality: %s", x$target),
sprintf("Predicted: %s", predict(myboostedclassifier, x)))
## Do a streaming prediction
stream_in(con = myjsondataset,
handler = function(x){
x <- datatransfo(x)
myprediction <- predict(myboostedclassifier, x)
## Basic evaluation by extracting accuracy
print(round(sum(myprediction == x$target) / length(myprediction), 2))
},
pagesize = 100)
For more information on RMOA or streaming modelling, get into contact.




