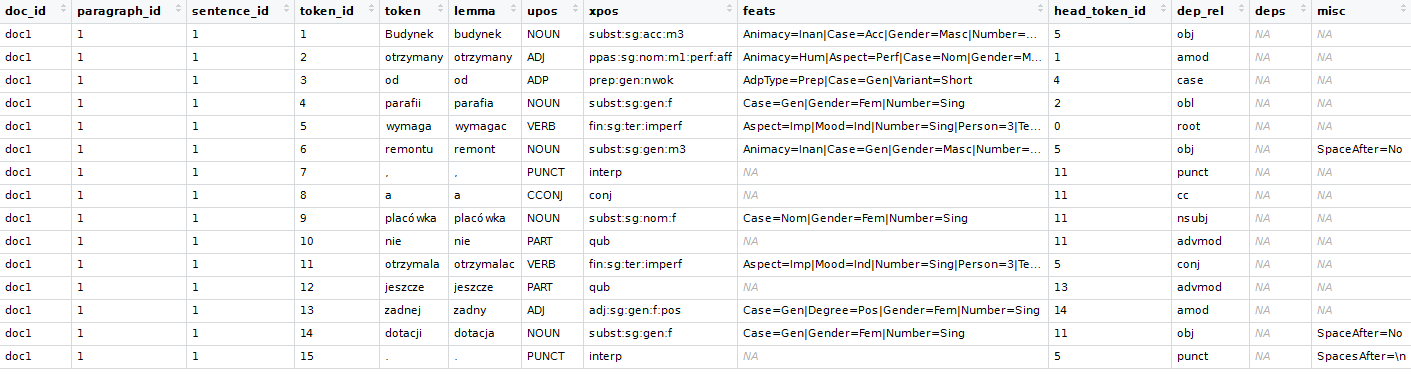
A comparison between spaCy and UDPipe for Natural Language Processing for R users
In the last few years, Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become more and more an open multi-lingual task instead of being held back by language, country and legal boundaries. With the advent of commonly used open data regarding natural language processing tasks as available at http://universaldependencies.org one can now relatively easily compare different toolkits which perform natural language processing. In this post we compare the udpipe R package to the spacyr R package.
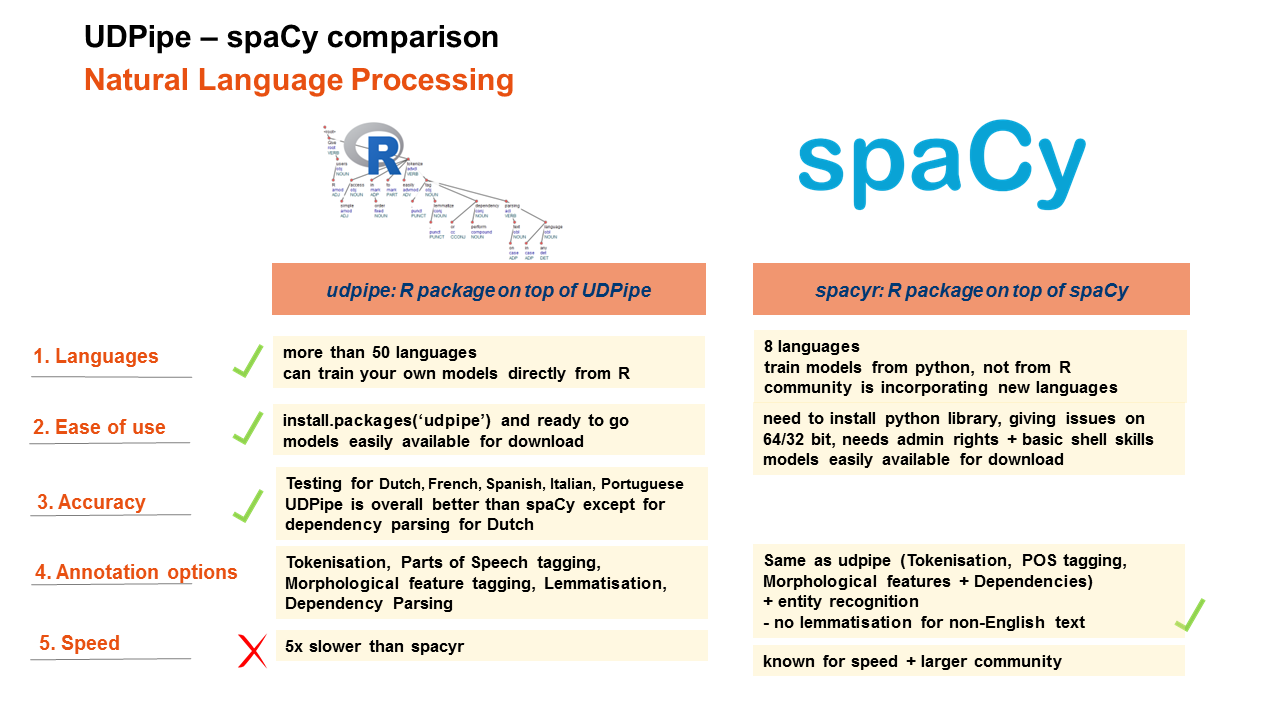
UDPipe - spaCy comparison
A traditional natural language processing flow consists of a number of building blocks which can be used to structure your Natural Language Application on top of it. Namely
1. tokenisation
2. parts of speech tagging
3. lemmatisation
4. morphological feature tagging
5. syntactic dependency parsing
6. entity recognition
7. extracting word & sentence meaning
Both of these R packages allow to do this where
- spacyr is an R package around the popular spaCy NLP toolkit: https://github.com/explosion/spaCy
- udpipe is an R package around the less known UDPipe NLP toolkit: https://github.com/ufal/udpipe
Comparison
In the comparison, we will provide general feedback on the following elements
- Languages which are covered by the tools
- Ease of use
- Annotation possibilities
- Annotation accuracy of the models
- Annotation speed
 Annotation languages
Annotation languages
- udpipe provides annotation models for more than 50 languages (afrikaans, ancient_greek-proiel, ancient_greek, arabic, basque, belarusian, bulgarian, catalan, chinese, coptic, croatian, czech-cac, czech-cltt, czech, danish, dutch-lassysmall, dutch, english-lines, english-partut, english, estonian, finnish-ftb, finnish, french-partut, french-sequoia, french, galician-treegal, galician, german, gothic, greek, hebrew, hindi, hungarian, indonesian, irish, italian, japanese, kazakh, korean, latin-ittb, latin-proiel, latin, latvian, lithuanian, norwegian-bokmaal, norwegian-nynorsk, old_church_slavonic, persian, polish, portuguese-br, portuguese, romanian, russian-syntagrus, russian, sanskrit, serbian, slovak, slovenian-sst, slovenian, spanish-ancora, spanish, swedish-lines, swedish, tamil, turkish, ukrainian, urdu, uyghur, vietnamese) of which 17 languages are released under a commercially more liberal license, the others are released under the CC-BY-SA-NC licence
- With the udpipe R package, you can furthermore directly train models on top of the newest CONLLU files available at http://universaldependencies.org (examples of this is provided at https://github.com/bnosac/udpipe.models.ud)
- spaCy provides currently models for 8 languages: English/German/Spanish/Portugues/French/Italian/Dutch.
- For English and German these were trained on data which is not available on http://universaldependencies.org, for the other models they were trained on data from http://universaldependencies.org
- In order to train your own models you need to do this directly in Python, the Python community is building these since the end of 2017.
Ease of use
- Both packages are on CRAN
- Models can be easily downloaded with both packages. For udpipe this is directly from R, for spacy this needs to be done in Python.
- udpipe has no external dependencies and can easily be installed with install.packages('udpipe') and next you are ready to go
- installation of spacyr will probably give you some trouble namely it
- requires installation of the Python package spacy which is more difficult to install on a local computer in your corporate office. You can easily get stuck in problems of Python versioning, 32 vs 64 bit architecture issues, admin rights or basic shell commands that you should be aware of
- does not allow to switch seamlessly between 2 languages (you need to initialize and finalize) which is a burden if you live in a multi-language country like e.g. Belgium
- spaCy models are constructed on different treebanks each following different guidelines which make cross-language downstream analysis more difficult to harmonise
Annotation accuracy of the models
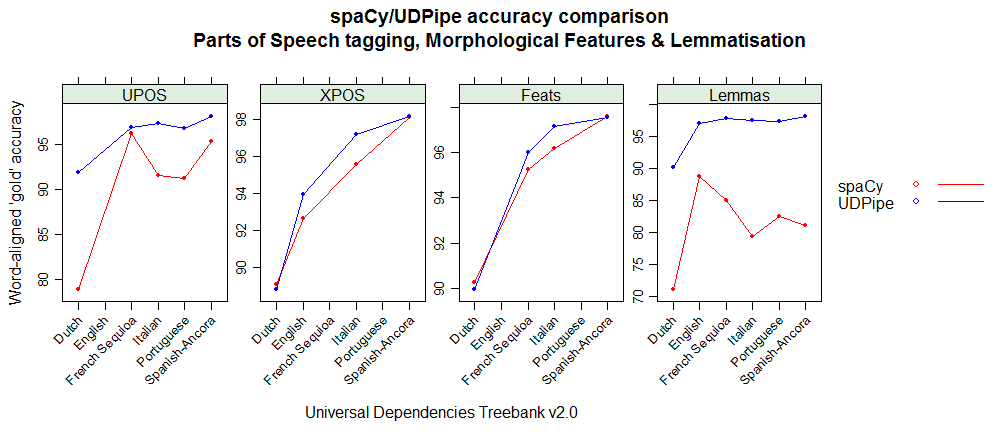
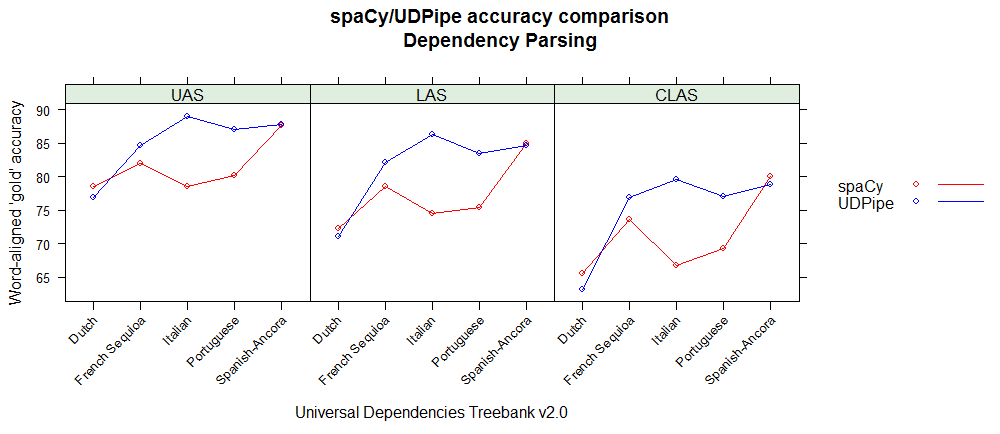
As the spaCy and UDPipe models for Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian and Dutch have been built on data from the same Universal Dependencies treebank (version 2.0) one can compare the accuracies of the different NLP processing steps (tokenisation, POS tagging, morphological feature tagging, lemmatisation, dependency parsing).
Evaluation is traditionally done by leaving out some sentences from the training part and seeing how good the model did on these hold-out sentences which were tagged by humans that's why they are called 'gold'.
Below you can find accuracy statistics for the different NLP tasks by using the conllu 2017 shared task evaluation script on the holdout test sets. These graphs basically show that
- UDPipe provides better results for French, Italian & Portuguese, equal results for Spanish and less good results for dependency parsing and treebank-specific tags for Dutch but better results for the universal parts of speech tags.
- For English, only the Penn Treebank XPOS tag can be compared and spaCy shows less good results than what we expected when comparing to the UDPipe model
Exact reproducible details on the evaluation can be found at https://github.com/jwijffels/udpipe-spacy-comparison. Feel free to provide comments there.
Annotation possibilities
- udpipe
- allows to do tokenisation, parts of speech tagging, morphological feature tagging and dependency parsing
- udpipe does not provide entity recognition and does not provide word vectors (you can use existing R packages for that (e.g text2vec)
- spacyr
- spaCy allows to do tokenisation, parts of speech tagging, morphological feature tagging and dependency parsing
- On top of that it also does entity recognition
- spacyr does not provide lemmatisation
- spaCy also provides wordvectors (for English only) but they are not made available in spacyr
So if you need entity recognition, udpipe is not an option. If you need lemmatisation, spacyr is not an option.
Annotation speed
- spacyr is in our experiments 5 times faster than udpipe for a comparable full annotation pipeline (Tokenisation, POS tagging, Lemmatisation, Feature tagging, Dependency Parsing) and comparable output (see code below)
library(udpipe)
library(spacyr)
library(microbenchmark)
data(brussels_reviews, package = "udpipe")
f_udpipe <- function(x, model){
x_anno <- udpipe_annotate(model, x = x)
x_anno <- as.data.frame(x_anno)
invisible()
}
f_spacy <- function(x){
x_anno <- spacy_parse(x, pos = TRUE, tag = TRUE, lemma = TRUE, entity = FALSE, dependency = TRUE)
invisible()
}
## Dutch
x <- subset(brussels_reviews, language == "nl")
x <- x$feedback
ud_model <- udpipe_download_model(language = "dutch")
ud_model <- udpipe_load_model(ud_model$file)
spacy_initialize(model = "nl", python_executable = "C:/Users/Jan/Anaconda3/python.exe")
microbenchmark(
f_udpipe(x, model = ud_model),
f_spacy(x),
times = 2)
spacy_finalize()
Enjoy
Hope this provides you some guidance when you are thinking about extending your nlp workflow with more deeper natural language processing than merely sentiment analysis.